Living with both Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can be incredibly challenging. These conditions often overlap, making diagnosis and treatment complex.
At Spark Mental Health, we understand the importance of finding the right medications for BPD and ADHD to manage symptoms effectively. In this post, we’ll explore various medication options for both disorders, helping you navigate the path to better mental health.
Understanding BPD and ADHD Comorbidity
Prevalence of BPD and ADHD Co-occurrence
The overlap between Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) occurs more frequently than many people expect. This significant co-occurrence presents unique challenges for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Shared Symptoms and Diagnostic Challenges
The similarity of symptoms between BPD and ADHD complicates diagnosis and treatment. Both conditions involve impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, and difficulty in maintaining stable relationships. This overlap can lead to misdiagnosis or underdiagnosis of one condition when the other is present.
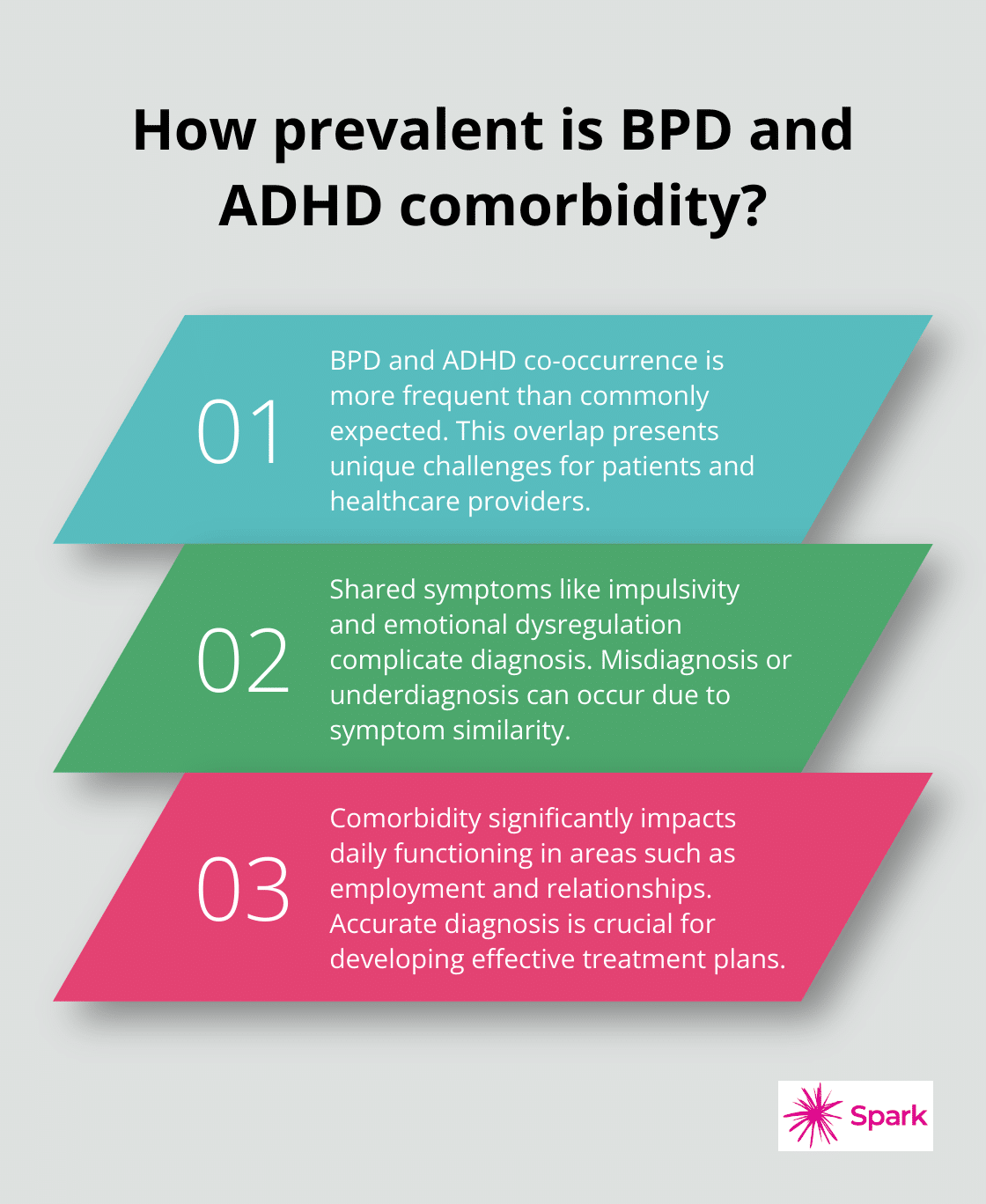
For instance, emotional instability (often associated with BPD) can be mistaken for mood swings sometimes seen in ADHD. Similarly, healthcare professionals might attribute the impulsivity characteristic of ADHD to BPD traits. This confusion can result in inadequate treatment plans that fail to address the full spectrum of a patient’s needs.
Impact on Daily Functioning
The combination of BPD and ADHD can profoundly affect a person’s quality of life. Individuals with both conditions often struggle with:
- Employment maintenance (due to focus difficulties and interpersonal relationship issues)
- Romantic partnership sustainability (because of emotional volatility and impulsive behaviors)
- Financial management (as a result of impulsive spending and disorganization)
- Academic success (due to attention problems and emotional instability)
These challenges can create a cycle of disappointment and frustration, further exacerbating the symptoms of both disorders.
The Need for Accurate Diagnosis
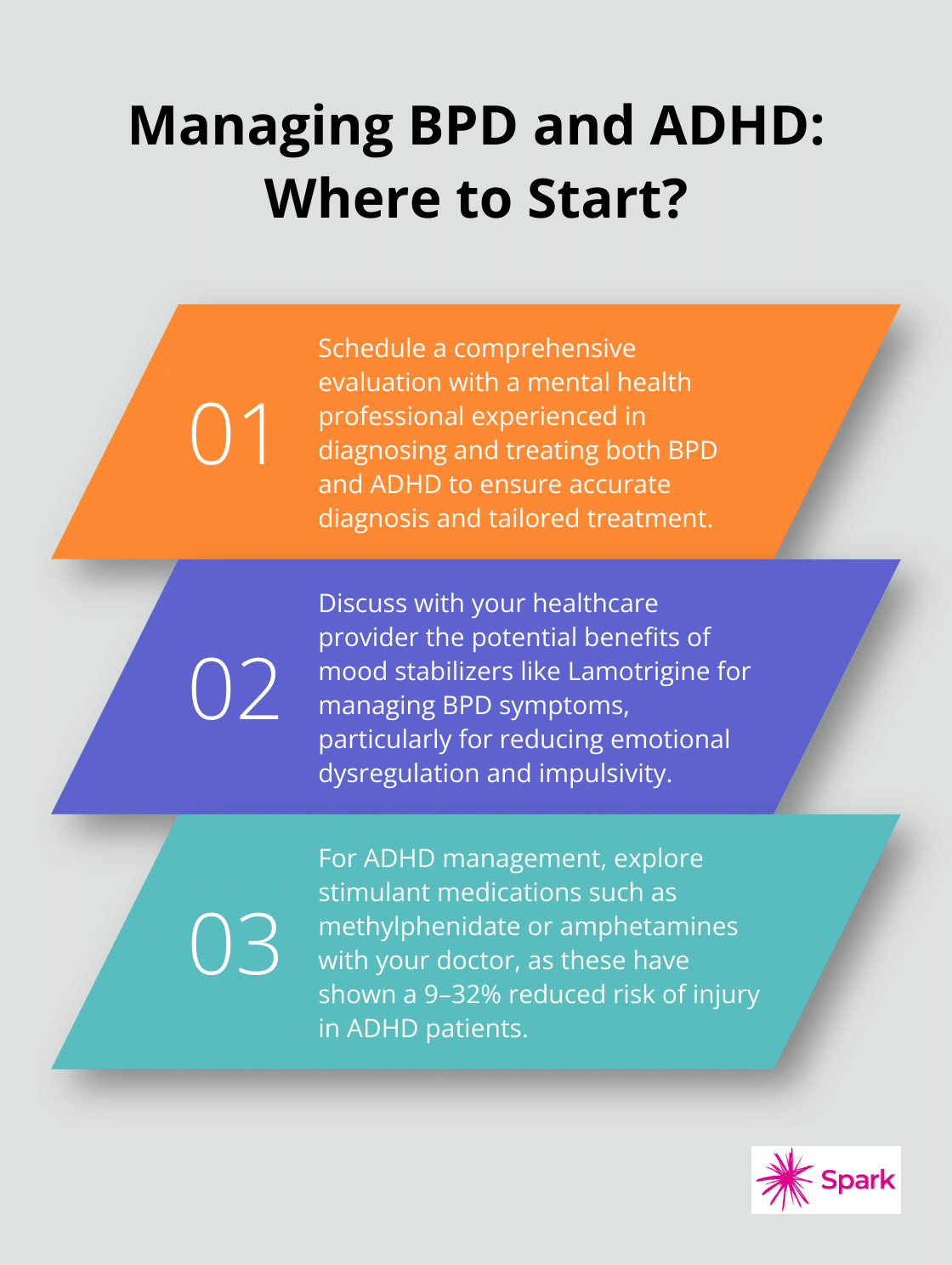
Given the complexity of BPD and ADHD comorbidity, patients should seek a comprehensive evaluation from a mental health professional experienced in diagnosing and treating both conditions. A thorough assessment that considers the full range of symptoms and their impact on daily functioning forms the foundation of effective treatment.
Accurate diagnosis serves as the first step towards effective treatment. Once healthcare providers properly identify both conditions, they can develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses the unique needs of each individual. This plan may include a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications designed to manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
As we move forward, we’ll explore the various medication options available for managing BPD and ADHD, starting with treatments specifically targeted at BPD symptoms.
Medication Options for BPD
Mood Stabilizers: A Primary Treatment Approach
Lamotrigine has shown promise in managing BPD symptoms, particularly in stabilizing mood and reducing emotional dysregulation and impulsivity. These medications regulate emotional volatility, a key symptom of BPD. Lithium, for example, reduces suicidal behaviors significantly.
Lamotrigine, another effective mood stabilizer, targets impulsivity and anger. Research revealed that lamotrigine reduced these symptoms when added to usual care for people receiving secondary care mental health services for BPD.
Antipsychotics: Addressing Specific BPD Symptoms
While not typically the first choice, antipsychotics benefit certain BPD symptoms. Low-dose quetiapine reduces cognitive-perceptual symptoms and anger. A study in the American Journal of Psychiatry reported a 33% decrease in hostility scores among BPD patients over six months.
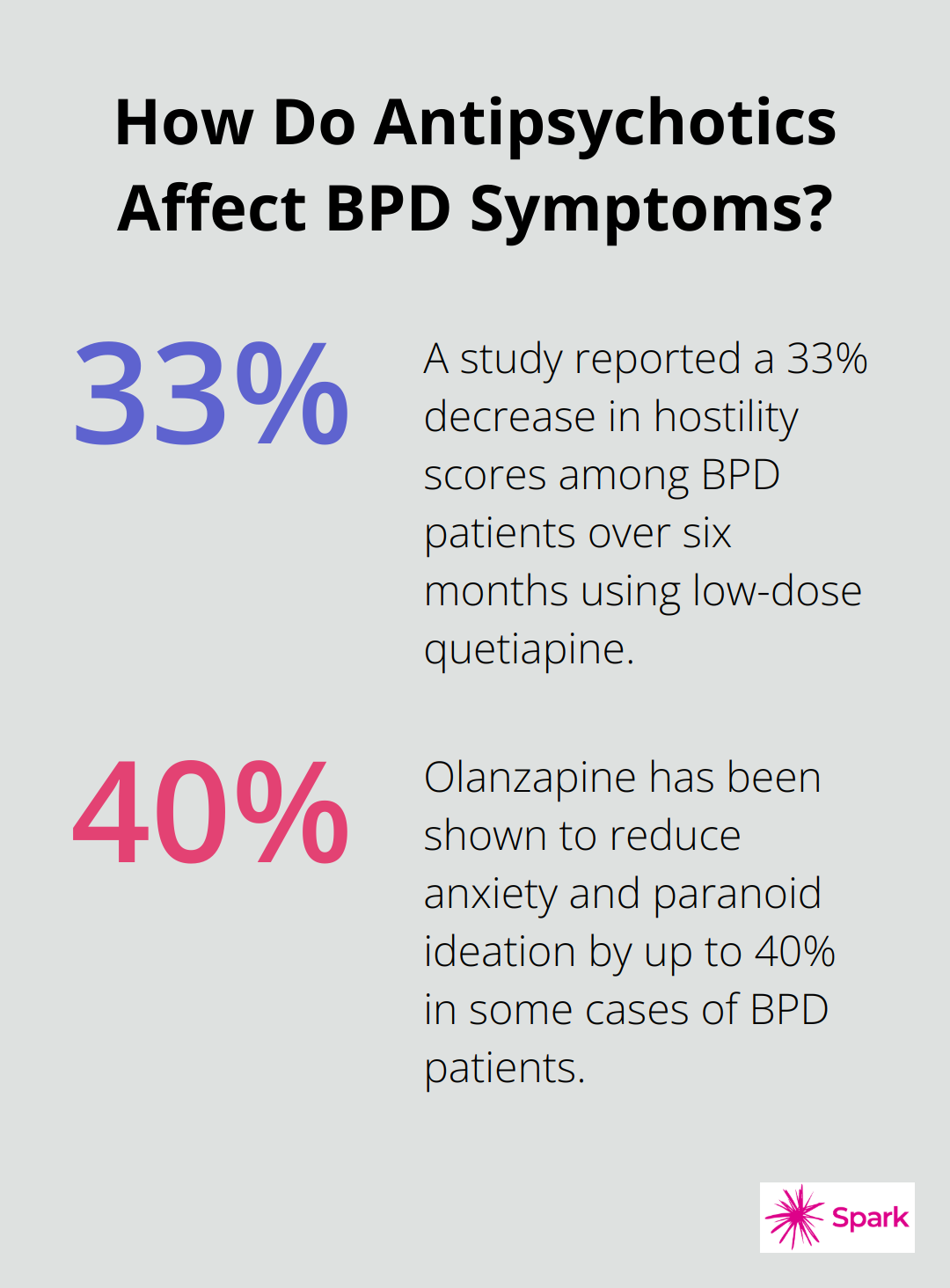
Olanzapine, another antipsychotic, proves effective in reducing anxiety and paranoid ideation (by up to 40% in some cases). However, the potential for significant side effects means antipsychotics are usually prescribed when other treatments haven’t succeeded.
Antidepressants: Managing Depressive Symptoms
Antidepressants, particularly SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors), help manage depressive symptoms often associated with BPD. A study investigated the association between response of impulsivity to treatment with fluoxetine and 5-HTTLPR polymorphism in 49 personality disordered patients.
It’s important to note that antidepressants alone rarely suffice for comprehensive BPD treatment. They work best when combined with other medications and psychotherapy.
Personalized Medication Approaches
A personalized approach to medication yields the best results in BPD treatment. What works for one patient may not work for another. Experienced psychiatrists should evaluate each patient’s unique symptoms and needs to develop an effective medication plan.
Medication represents just one part of a comprehensive BPD treatment plan. Psychotherapy, particularly Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), often complements medication for optimal results. As we explore medication options for ADHD in the next section, we’ll see how treating comorbid conditions requires a nuanced approach.
ADHD Medications That Work
Stimulant Medications: The Primary Treatment Option
Stimulants stand as the first choice for ADHD treatment due to their high effectiveness. These medications increase dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, which improves focus and reduces hyperactivity. Studies have found that ADHD medication was significantly associated with a 9–32% reduced risk of injury.

The two main types of stimulants are methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) and amphetamines (Adderall, Vyvanse). These come in various formulations, including immediate-release and extended-release options. The selection between these depends on individual needs and daily routines.
While highly effective, stimulants can have side effects such as decreased appetite, sleep problems, and (in rare cases) increased blood pressure. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider helps manage these potential side effects.
Non-Stimulant Options: Alternatives for Specific Cases
For those who don’t respond well to stimulants or have contraindications, non-stimulant medications offer an alternative. These include atomoxetine (Strattera), guanfacine (Intuniv), and bupropion (Wellbutrin). Typical antipsychotics have been tried and found to have some efficacy, but the long-term side effects limit their use in ADHD.
Atomoxetine increases norepinephrine levels in the brain. It’s particularly useful for patients with comorbid anxiety disorders, as it doesn’t exacerbate anxiety symptoms like stimulants sometimes do.
Guanfacine, originally developed as a blood pressure medication, shows efficacy in managing ADHD symptoms, particularly in children and adolescents. It helps reduce hyperactivity and impulsivity.
Bupropion, an antidepressant, has off-label use for ADHD. It benefits patients with comorbid depression or those trying to quit smoking.
Tailoring Treatment: A Personalized Approach
ADHD treatment isn’t one-size-fits-all. A thorough approach involves careful assessment of each patient’s symptoms, lifestyle, and any co-existing conditions. Many healthcare providers start with a low dose of medication and adjust as needed, closely monitoring for effectiveness and side effects.
In some cases, combining medications yields the best results. Improvements in ADHD symptom control with drug combinations were reported in most studies, except for one prospective double-blind, randomized study.
The Role of Medication in ADHD Management
Medication represents just one part of ADHD management. Experts recommend combining pharmacological treatment with behavioral strategies and lifestyle modifications for optimal results. A comprehensive treatment plan often includes therapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy) and lifestyle adjustments (like improved sleep habits and organizational techniques).
Final Thoughts
Managing BPD and ADHD simultaneously requires a personalized approach, especially when it comes to medications for BPD and ADHD. Each person’s experience with these conditions differs, necessitating a tailored treatment strategy. Medications play a vital role in symptom management but work best when combined with therapy and lifestyle adjustments.
Finding the right combination of treatments can challenge patients, but the effort pays off. Integrating medication with therapeutic approaches like Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) for BPD or Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for ADHD can enhance treatment outcomes significantly. These therapies provide valuable skills for emotional regulation, impulse control, and improved focus.
At Spark Mental Health, we offer personalized telepsychiatry services, including medication management and therapy, for conditions like BPD and ADHD. Our team of professionals commits to providing accessible, evidence-based care to help you navigate your mental health journey effectively. Take that first step towards better mental health today – you deserve it.






