The landscape of weight loss treatment is rapidly evolving. At Spark Healthcare, we’re excited to share the latest weight loss medication news that’s reshaping obesity care.
Recent breakthroughs have introduced powerful new drugs and combination therapies, offering hope to millions struggling with weight management. These advancements are not only more effective than traditional methods but also target specific genetic factors in obesity.
What Are the Latest Weight Loss Medications?
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A New Era in Weight Management
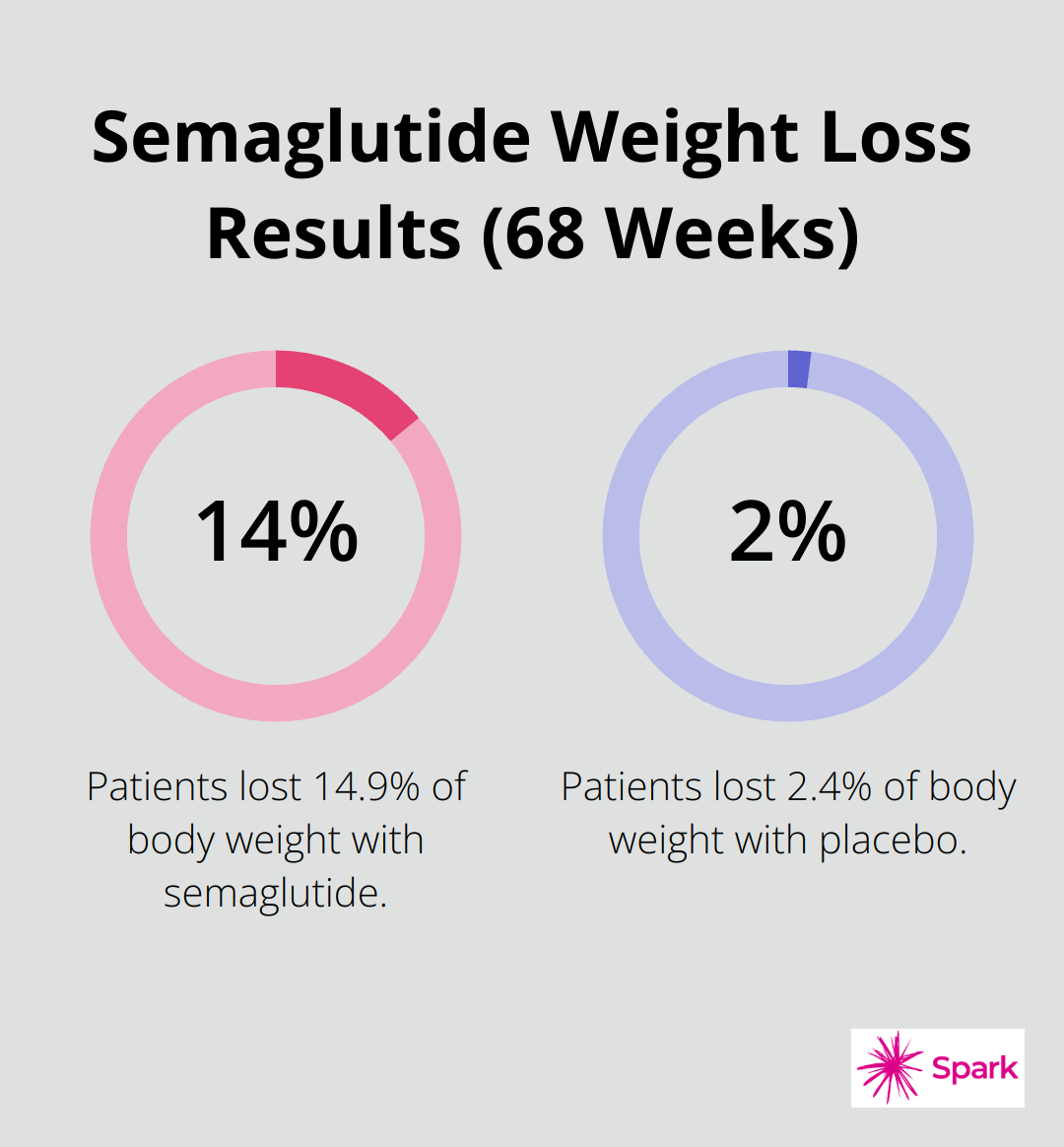
Semaglutide and tirzepatide lead the charge in GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs mimic a hormone that targets areas of the brain involved in appetite regulation. Semaglutide (marketed as Wegovy for weight loss) has shown impressive results. Clinical trials report patients lost an average of 14.9% of their body weight over 68 weeks compared to 2.4% with placebo. Tirzepatide (sold as Mounjaro for diabetes) has demonstrated even more striking outcomes. Some studies report weight loss of up to 22.5% in participants.
Combination Therapies: Tackling Weight Loss from Multiple Angles
Phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia) and naltrexone-bupropion (Contrave) represent a new approach. These medications combine drugs with different mechanisms to enhance weight loss effects. Qsymia pairs a stimulant with an anti-seizure medication, while Contrave combines an opioid antagonist with an antidepressant. Randomized controlled trial evidence demonstrates that these medications, along with semaglutide and liraglutide, all reduce body weight compared with placebo when combined with lifestyle interventions.
Targeting Genetic Obesity: Setmelanotide’s Breakthrough
For a small subset of patients with rare genetic obesity disorders, setmelanotide (Imcivree) offers new hope. This medication targets the melanocortin-4 receptor pathway, which plays a key role in weight regulation. Clinical experts agree that setmelanotide would be considered a first-line therapy for patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome who have hyperphagia and obesity.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes
These new medications represent major advancements, but they’re not magic pills. They work best when combined with lifestyle changes. A comprehensive approach to weight management should include diet, exercise, and behavioral modifications alongside any medication regimen.
Side Effects and Considerations
It’s important to note that these drugs can have side effects. Common issues include nausea, diarrhea, and constipation. Some patients may experience more serious complications (such as pancreatitis or gallbladder problems). Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine if these medications are right for you.
As we explore these new frontiers in weight loss treatment, the potential to help more patients achieve their health goals grows. The next chapter will examine the efficacy and safety of these new weight loss drugs in more detail, comparing them to traditional methods and discussing long-term considerations.
How Effective Are New Weight Loss Drugs?
Clinical Trial Results
The latest weight loss medications have shown remarkable results in clinical trials. Semaglutide led to an average weight loss of 14.9% over 68 weeks. This surpasses the 2-3% weight loss typically seen with traditional diet and exercise alone.
Tirzepatide demonstrated even more impressive outcomes. The SURMOUNT-1 trial reported substantial and sustained reductions in body weight over 72 weeks. This level of weight loss rivals the results often seen after bariatric surgery (traditionally considered the most effective treatment for severe obesity).
Real-World Effectiveness
While clinical trials provide controlled data, real-world results can differ. A 2023 study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association examined semaglutide’s effectiveness in a real-world setting. Patients lost an average of 6.1% of their body weight after 3 months and 10.9% after 6 months. Although slightly lower than clinical trial results, these outcomes still represent significant improvements over traditional methods.
Comparison with Traditional Methods
Traditional weight loss methods typically result in 5-10% weight loss over 6-12 months. However, many find long-term maintenance challenging. The new medications appear to facilitate greater initial weight loss and help maintain it.
A 2022 meta-analysis in the Lancet compared various weight loss interventions. It found that pharmacotherapy combined with lifestyle changes resulted in an average of 11% weight loss at one year, compared to 5% with lifestyle changes alone.

Safety Considerations
These new medications show promise but come with side effects. Gastrointestinal adverse events affect patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists. These include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea (usually mild to moderate and improving over time).
More serious but rare side effects have been reported. Semaglutide may increase the risk of pancreatitis and gallbladder problems. Tirzepatide has been associated with a small increased risk of thyroid C-cell tumors in rodents, though its relevance to humans remains unclear.
Long-Term Safety
Long-term safety data for these newer medications remains limited. The longest studies to date have followed patients for about two years. While the results are encouraging, more research will uncover the effects of these drugs over many years or decades of use.
Patients must work closely with healthcare providers when using these medications. Regular monitoring can catch potential issues early and ensure the benefits continue to outweigh any risks.
The next chapter will explore how these new medications are changing the landscape of obesity treatment and management, and discuss their potential to reduce obesity-related health complications.
How New Medications Transform Obesity Care
Redefining Obesity Treatment
The introduction of potent new weight loss medications has fundamentally altered the approach to obesity treatment. These drugs are not mere tools for weight reduction; they reshape our understanding of obesity as a chronic disease that requires long-term management.
Traditionally, obesity treatment focused primarily on diet and exercise. While these remain essential components, the new medications offer a more comprehensive approach. They target biological pathways that influence appetite and metabolism, addressing the underlying mechanisms of weight gain.
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide work by mimicking hormones that regulate hunger and satiety. This biological approach helps patients feel fuller for longer, which makes adherence to calorie-restricted diets easier.
Synergy of Medication and Lifestyle Changes
These new medications produce optimal results when integrated with lifestyle interventions. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that combining semaglutide with intensive behavioral therapy led to an average weight loss of 16% after 68 weeks (compared to 5.7% with placebo).
Weight management programs that combine medication (when appropriate) with personalized nutrition plans, exercise regimens, and behavioral counseling offer a comprehensive strategy. This approach addresses not just the physical aspects of weight loss, but also the psychological and emotional factors that influence eating habits.
Addressing Obesity-Related Health Issues
The potential of these new medications to reduce obesity-related comorbidities is perhaps their most exciting aspect. A 2024 study published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology reported that patients taking tirzepatide for one year showed significant improvements in cardiovascular risk factors (including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and insulin sensitivity).
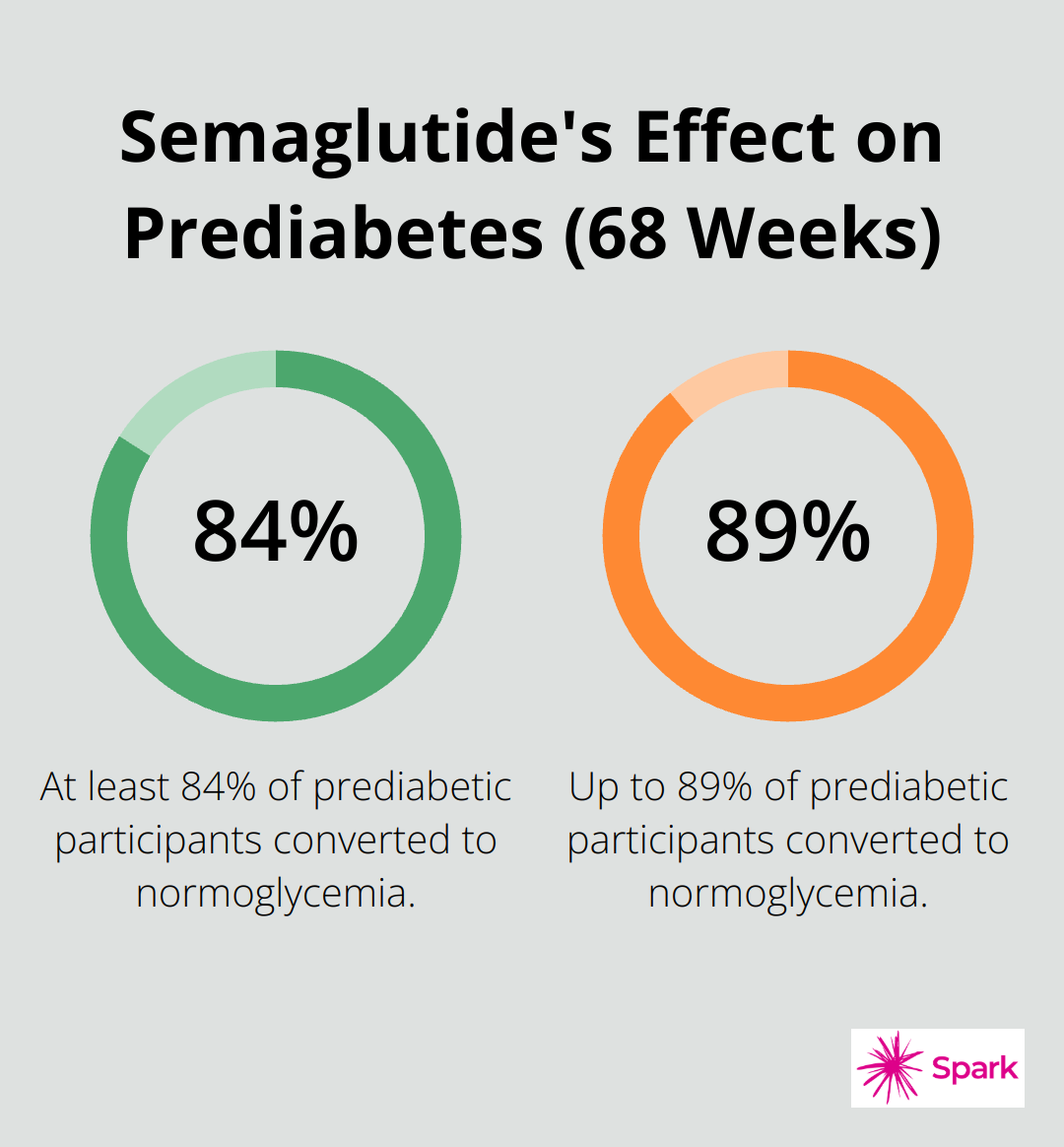
Moreover, these medications may help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes in at-risk individuals. The STEP 1 trial, which evaluated semaglutide, found that 84% to 89% of participants with prediabetes had converted to normoglycemia after 68 weeks of treatment.
The impact extends beyond metabolic health. Emerging research suggests these medications may also improve outcomes for conditions like sleep apnea, osteoarthritis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A 2025 meta-analysis in Obesity Reviews found that GLP-1 receptor agonists led to significant improvements in liver function tests and reduced liver fat content in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Personalized Treatment Approaches
While these new medications represent a significant leap forward in obesity treatment, they’re not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each patient’s journey is unique, and treatment plans should be tailored to individual needs, preferences, and medical histories.
As we continue to learn more about these drugs and their long-term effects, their potential to improve health outcomes for millions struggling with obesity becomes increasingly clear. The future of obesity care lies in personalized, comprehensive approaches that combine the power of these new medications with targeted lifestyle interventions.
Final Thoughts
The landscape of weight loss treatment has transformed dramatically in recent years. New medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists and combination therapies have set a new standard for efficacy, offering hope to millions struggling with obesity. These advancements represent a significant leap forward in our ability to address this complex health issue.
Clinical trials and real-world data demonstrate the impressive potential of these new treatments. Medications such as semaglutide and tirzepatide show weight loss results that rival surgical interventions, while also improving various obesity-related health conditions. This marks a paradigm shift in obesity management, moving from a focus solely on weight to a more holistic view of metabolic health.
The future of pharmaceutical obesity treatment looks bright, with researchers exploring new drug targets, improved delivery methods, and personalized approaches. At Spark Healthcare, we emphasize the importance of combining pharmacological interventions with lifestyle modifications for long-term success. For those seeking support in their weight loss journey or dealing with related mental health concerns, Spark Mental Health offers personalized, evidence-based telepsychiatry services.






