Bipolar disorder affects millions worldwide, presenting unique challenges in treatment and daily life. At Spark Healthcare, we understand the complex relationship between bipolar medication and weight management.
Many individuals struggle to balance mood stability with potential side effects, including weight gain. This blog post explores the connection between bipolar medications and weight changes, offering practical strategies for maintaining a healthy weight while effectively managing bipolar symptoms.
What Is Bipolar Disorder and How Is It Treated?
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings. People with bipolar disorder often experience periods of extremely “up,” elated, irritable, or energized behavior (known as manic episodes) and very “down,” sad periods. These swings range from manic highs to depressive lows, significantly impacting daily life.
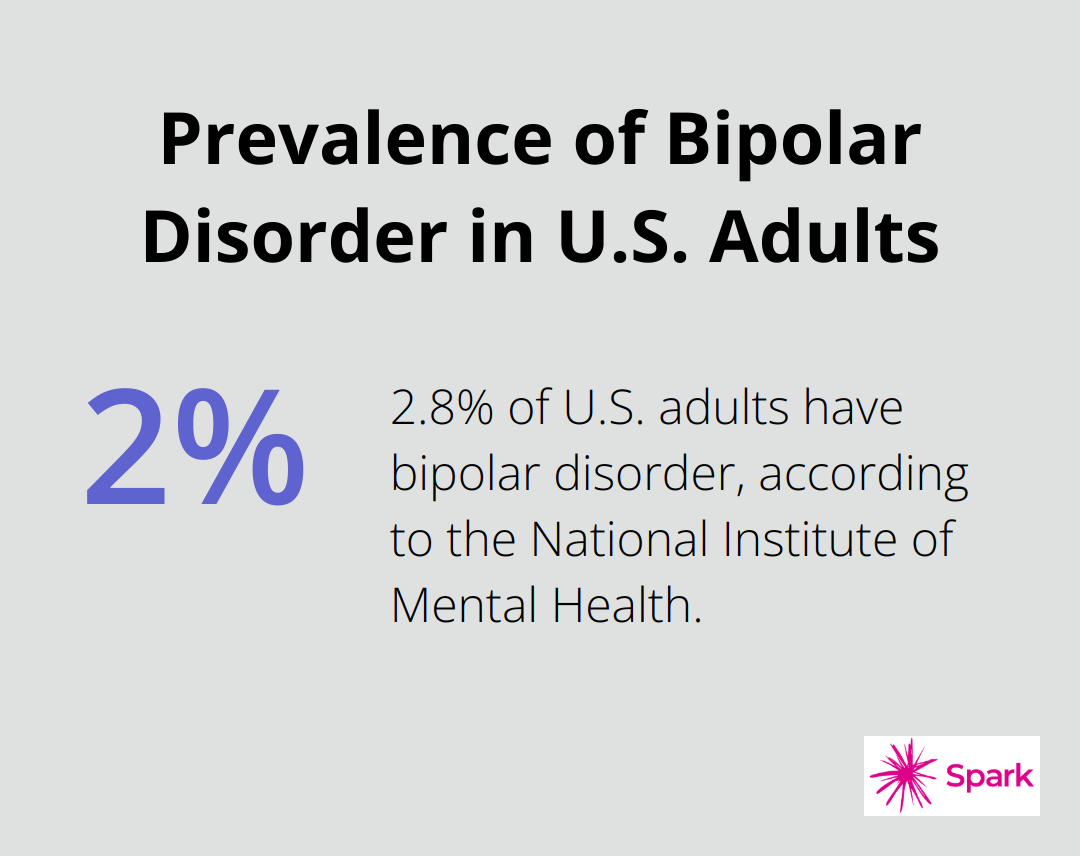
Approximately 2.8% of U.S. adults have bipolar disorder, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. This condition often emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood, with an average onset age of 25 years (although some individuals may experience symptoms as early as childhood or as late as their 50s).
The Importance of Medication
Medication plays a pivotal role in managing bipolar disorder. Without proper treatment, individuals with bipolar disorder face a significant risk of suicide, with research indicating that up to 20% of mostly untreated bipolar disorder subjects end their life by suicide, and 20-60% attempt suicide at least once. This highlights the urgent need for effective interventions. The right medication can stabilize mood swings, reduce the frequency and severity of episodes, and improve overall quality of life.
Types of Medications
Several types of medications are commonly used to treat bipolar disorder:
- Mood stabilizers (e.g., lithium): These remain a cornerstone of treatment.
- Anticonvulsants: Originally developed to treat epilepsy, these have also shown effectiveness in managing bipolar symptoms.
- Atypical antipsychotics: Often used to treat both manic and depressive episodes.
Personalized Treatment Approaches
No two cases of bipolar disorder are identical. That’s why personalized treatment plans are essential. For instance, while lithium is highly effective for many, it may not be suitable for everyone. Lamotrigine has shown effectiveness in reducing the risk of depressive relapse in stabilized bipolar patients, according to evidence from randomized, controlled trials.
Ongoing Monitoring and Management
Effective bipolar treatment isn’t just about finding the right medication-it’s about ongoing management. Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider are essential. These appointments allow for medication adjustments, side effect management, and overall health monitoring. Blood tests may be necessary to check medication levels and ensure optimal dosing.
While medication is a key component of bipolar disorder treatment, it’s most effective when combined with psychotherapy and lifestyle changes. A holistic approach that addresses all aspects of an individual’s life tends to yield the best outcomes. As we move forward, we’ll explore the specific link between bipolar medications and weight changes, a common concern for many patients.
Why Bipolar Medications Affect Weight
The Science Behind Medication-Induced Weight Gain
Bipolar medications, while essential for managing mood swings, often cause unwanted weight gain. This weight change can occur rapidly, sometimes within weeks of starting treatment. The mechanisms behind this weight gain are complex and vary depending on the specific medication.
Bipolar medications alter brain chemistry, which affects appetite and metabolism. In bipolar disorder, neurotransmitters are abnormally regulated in the brain, and biogenic amine neurotransmission functions in the limbic system are impaired.
Lithium, a common mood stabilizer, can cause fluid retention, leading to a quick initial weight gain. However, recent research suggests that weight gain with lithium may not be as significant as previously thought.
Atypical antipsychotics, particularly olanzapine and quetiapine, cause significant weight gain. A meta-analysis in the Archives of General Psychiatry found that patients on olanzapine gained an average of 4.45 kg (9.8 pounds) after 10 weeks of treatment.
Medications and Their Weight Effects
Not all bipolar medications affect weight equally. Here’s a breakdown of common medications and their typical effects:
- Lithium: Moderate weight gain
- Valproic acid: Significant weight gain
- Carbamazepine: Minimal weight change
- Lamotrigine: Generally weight-neutral
- Olanzapine: Significant weight gain
- Quetiapine: Moderate to significant weight gain
- Risperidone: Moderate weight gain
- Aripiprazole: Minimal weight change
It’s important to note that individual responses can vary. Some people may experience significant weight gain on a medication that typically causes minimal changes, while others may maintain their weight on medications associated with gain.
The Impact on Treatment and Health
Weight gain from bipolar medications isn’t just a cosmetic concern-it can have serious implications for both treatment adherence and overall health.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that weight gain was the most common reason for medication non-adherence among bipolar patients, with 62% of patients reporting it as a major concern. This non-adherence can lead to relapse of bipolar symptoms, potentially resulting in hospitalization or other serious consequences.

Moreover, significant weight gain increases the risk of developing other health problems. These include:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease
- High blood pressure
- Sleep apnea
- Certain types of cancer
A large-scale study published in JAMA Psychiatry found that individuals with bipolar disorder have a 1.7 times higher risk of cardiovascular mortality compared to the general population, partly due to medication-induced weight gain and metabolic changes.
Balancing Medication Efficacy and Weight Management
Finding the right balance between effective symptom management and minimizing side effects is a challenge. In some cases, this might involve trying different medications or combinations to find the most effective treatment with the least impact on weight.
It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor weight changes and adjust treatment plans as needed. This collaborative approach can help address both bipolar symptoms and weight concerns effectively.
The next section will explore practical strategies for managing weight while on bipolar medication, including lifestyle modifications and potential medication adjustments that can help mitigate weight gain without compromising treatment efficacy.
How to Manage Weight on Bipolar Medication
Collaborate with Your Healthcare Provider
Open communication with your healthcare provider is essential. Discuss your weight concerns and work together to find a medication regimen that balances mood stability and weight management. Some newer medications, like lurasidone, have shown minimal impact on weight. Six-month open-label extension trials of lurasidone have demonstrated that the weight gained during 6 weeks of exposure to olanzapine can be reversed.
If you experience significant weight gain, your provider might consider adjusting your medication. For instance, switching from olanzapine to aripiprazole could help. A study found that maximum weight gain was seen with olanzapine treatment, while it was least with aripiprazole and ziprasidone.
Implement Lifestyle Changes
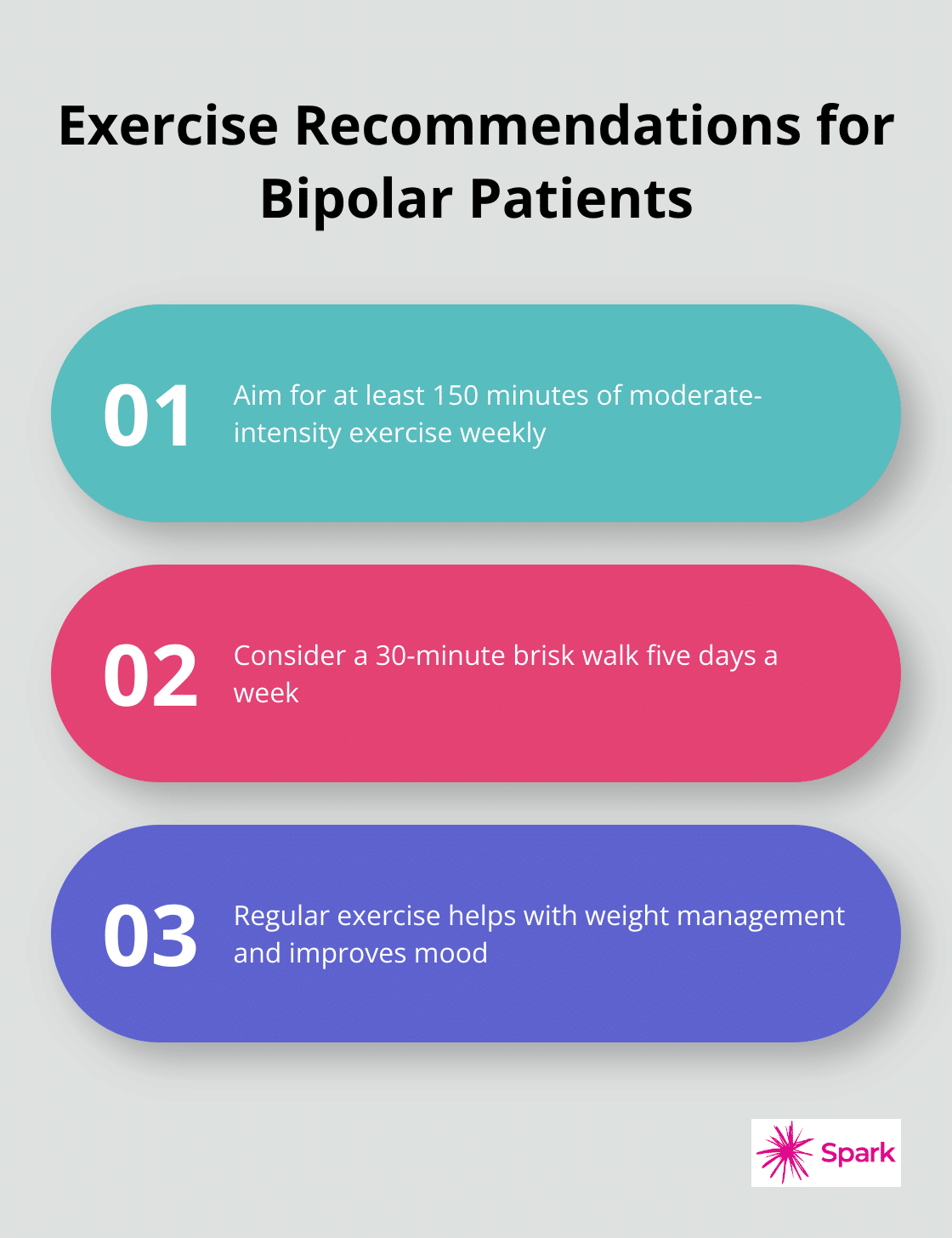
Lifestyle modifications play a key role in managing weight. The National Institute of Mental Health recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly. This could involve a 30-minute brisk walk five days a week. Exercise not only helps with weight management but also improves mood and overall well-being.
Sleep hygiene is another critical factor. Poor sleep can lead to weight gain and mood instability. Try to get 7-9 hours of sleep per night and maintain a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends.
Optimize Your Nutrition
Diet significantly impacts weight management. Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. A recent study compared the effects of time-restricted eating versus Mediterranean diet on symptoms and quality of life in bipolar disorder.
Mindful eating can also help. Use smaller plates, eat slowly, and pay attention to hunger and fullness cues. Avoid skipping meals, as this can lead to overeating later.
Consider working with a registered dietitian who specializes in mental health. They can create a personalized meal plan that supports both your weight goals and mental health needs.
Explore Additional Support Options
Telehealth services (including access to mental health professionals and nutritionists) can provide personalized advice for managing bipolar depression and weight. These services offer convenience and flexibility, allowing you to receive support from the comfort of your home.
Monitor Progress and Adjust Strategies
Regular check-ins with your healthcare team are important. Keep track of your weight, mood, and any side effects you experience. This information helps your provider make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Be prepared to adjust your strategies as needed. What works for one person may not work for another, and what works at one point in your treatment may need to be modified later on.
Final Thoughts
Managing bipolar disorder while maintaining a healthy weight presents challenges, but individuals can achieve this goal. Medication adherence plays a vital role in mood stability and overall well-being. Addressing potential side effects, including weight gain, requires a comprehensive approach to treatment.
Spark Healthcare offers telepsychiatry services with personalized care plans, medication management, and cognitive-behavioral therapy to support individuals in their mental health journey. Our evidence-based approach aims to provide comprehensive care that addresses both mood stability and overall well-being, including concerns about bipolar medication and weight loss. Patients should work closely with healthcare providers, including psychiatrists, therapists, and nutritionists, to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Regular check-ins, open communication about side effects, and adjustments to strategies when necessary contribute to successful bipolar disorder management. With the right support and resources, patients can effectively manage their condition while maintaining a healthy weight. This approach allows individuals with bipolar disorder to work towards a balanced, fulfilling life.






