At Spark Mental Health, we’re excited about the potential breakthroughs in ADHD treatment on the horizon.
The landscape of ADHD medications is evolving rapidly, with new ADHD medications in 2025 promising improved efficacy and fewer side effects.
These advancements could revolutionize how we manage ADHD symptoms and enhance the quality of life for millions of individuals worldwide.
The Current ADHD Medication Landscape
Dominant Medication Classes
The ADHD medication market currently features two primary classes: stimulants and non-stimulants. Stimulants, including methylphenidate and amphetamines, serve as the first-line treatment for many patients. These medications increase dopamine levels in the brain, which improves focus and reduces hyperactivity. Non-stimulants, such as atomoxetine and guanfacine, provide an alternative for individuals who don’t respond well to stimulants or have contraindications.
Limitations of Existing Treatments
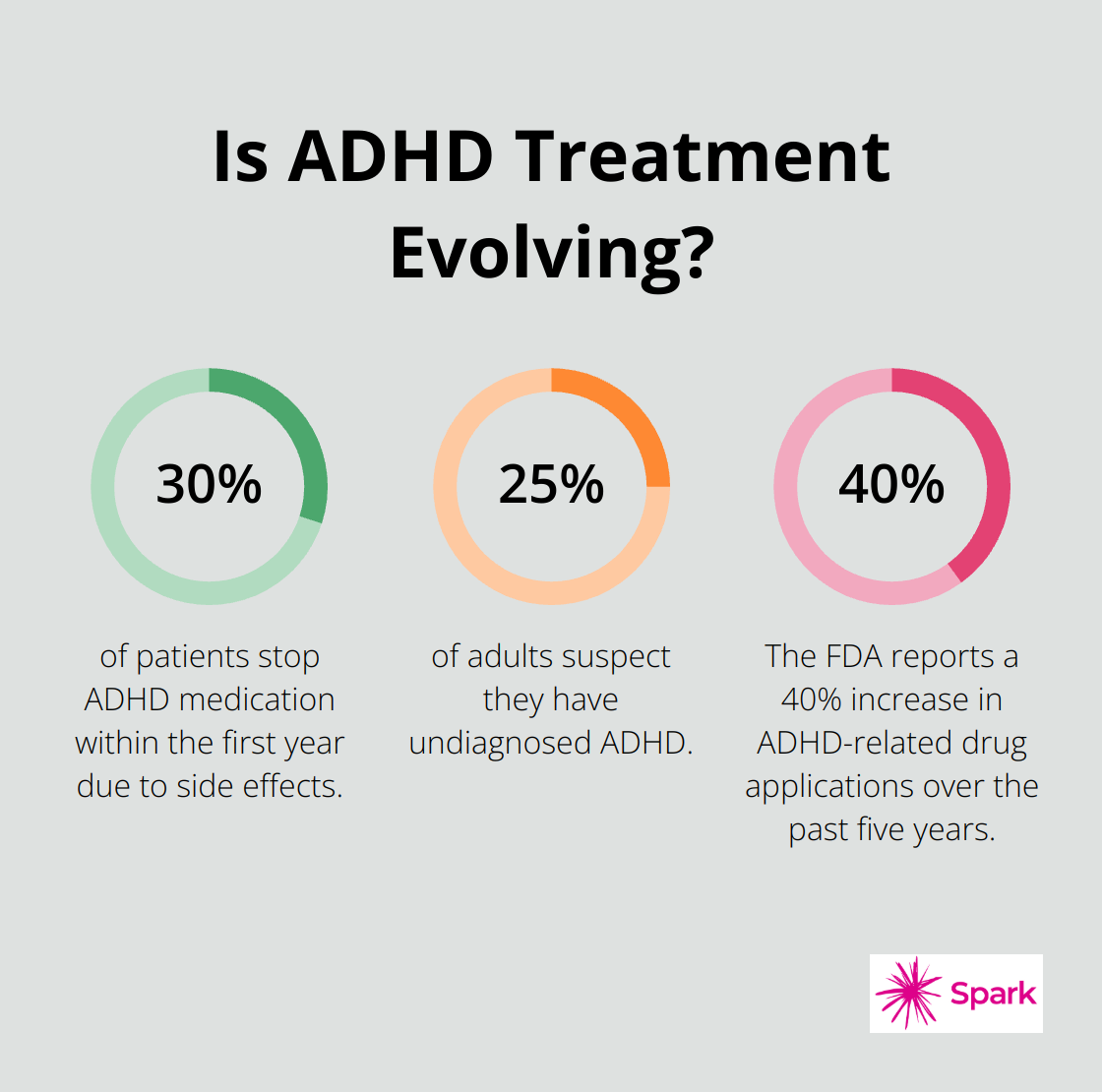
Current ADHD medications, while effective for many, present significant drawbacks. Side effects remain a major concern, with appetite suppression, sleep disturbances, and mood changes frequently reported. A 2024 study in the Journal of Attention Disorders revealed that up to 30% of patients stop medication within the first year due to side effects.
The short duration of action for many medications poses another challenge. Some patients require multiple doses throughout the day, which disrupts daily routines and leads to inconsistent symptom control. The American Academy of Pediatrics has published clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.
The Drive for Innovation
The demand for new ADHD medications is evident. Patients and healthcare providers seek treatments that offer longer-lasting effects, fewer side effects, and better management of comorbid conditions. A recent survey by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center found that 25% of adults suspect they have undiagnosed ADHD.
Pharmaceutical companies have responded to this demand. The FDA reports a 40% increase in ADHD-related drug applications over the past five years. These new medications try to address the gaps in current treatment options, potentially offering more targeted approaches to symptom management.
Emerging Trends in ADHD Treatment
Recent research has focused on developing medications with novel mechanisms of action. Scientists explore compounds that target specific neurotransmitter systems beyond dopamine and norepinephrine. These efforts aim to provide more precise symptom control and potentially address aspects of ADHD that current medications don’t fully manage.
Additionally, researchers investigate new delivery methods to improve medication adherence and effectiveness. Extended-release formulations and transdermal patches show promise in providing more consistent symptom control throughout the day. These innovations could reduce the need for multiple daily doses and minimize the “peaks and valleys” often experienced with current medications.
As the field of ADHD treatment continues to evolve, the next chapter will explore the promising medications currently in clinical trials. These potential breakthroughs may reshape the landscape of ADHD management in the coming years.
What’s New in ADHD Drug Development?
The landscape of ADHD treatment stands on the brink of significant change. Researchers explore innovative approaches to address the limitations of current medications. This chapter highlights the most promising developments in ADHD drug research and their potential impact on patient care.
Innovative Non-Stimulant Approaches
Several non-stimulant medications show promise in late-stage clinical trials. A selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) demonstrates potential for improved symptom control. A recent study assessed the effectiveness of SNRIs in managing ADHD symptoms, adding to our understanding of these medications.

Another exciting development targets the glutamate system. Early results indicate it may help with both attention deficits and emotional regulation, addressing a broader spectrum of ADHD symptoms. This could benefit the estimated 50-70% of adults with ADHD who also experience emotional dysregulation (according to a 2024 study in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry).
Revolutionary Delivery Methods
Researchers explore innovative ways to deliver existing ADHD medications more effectively. A transdermal patch for methylphenidate aims to provide steady medication release over 24 hours. The DAYTRANA patch is a long-acting ADHD treatment that can be removed early to fit a child’s individual needs.
An inhaled form of amphetamine is also under investigation. This rapid-onset formulation could offer more flexible dosing options, potentially allowing patients to manage symptoms as needed throughout the day. Early data suggests onset of action within 10-15 minutes (compared to 30-60 minutes for oral medications).
Promising Combination Therapies
The concept of combining different medications to target multiple aspects of ADHD gains traction. A notable trial investigates the synergistic effects of a stimulant medication with a non-stimulant alpha-2 agonist. Preliminary results indicate this combination may provide more comprehensive symptom control while allowing for lower doses of each medication, potentially reducing side effects.
Another intriguing study explores the combination of ADHD medication with a cognitive enhancer typically used in Alzheimer’s treatment. This approach aims to address not only core ADHD symptoms but also associated cognitive deficits that can persist even with traditional ADHD treatment. Interestingly, a recent study suggests that adult ADHD is associated with an increased risk of dementia, highlighting the importance of reliable assessment in adulthood.
The Path to Approval
While these developments show promise, it’s important to note that not all medications in clinical trials will reach the market. The FDA approval process remains rigorous, ensuring safety and efficacy before any new treatment becomes available.
As research progresses, the potential benefits of these new medications become clearer. The next chapter will explore how these innovations might improve the lives of individuals with ADHD and transform the landscape of ADHD management.
How New ADHD Medications Will Improve Patient Care
Reduced Side Effects
The next generation of ADHD medications promises significant improvements in patient care. These innovations address longstanding challenges associated with current treatments, potentially transforming the lives of individuals with ADHD.

One of the most anticipated benefits of emerging ADHD medications is the potential for fewer side effects. Current treatments, particularly stimulants, often result in unwanted effects. A review found that the use of stimulant medications raises the chances of cardiovascular diseases and is linked to an increase in resting heart rate and blood pressure.
New non-stimulant medications that target specific neurotransmitter systems may offer a more favorable side effect profile. For instance, the selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) in late-stage trials has shown promising results with fewer reported side effects in initial studies. This could lead to better medication adherence and improved quality of life for patients.
Longer-Lasting Symptom Control
Another significant advancement lies in the development of longer-lasting formulations. Many patients struggle with the “wear-off” effect of current medications, experiencing a return of symptoms before their next dose. The new transdermal patch for methylphenidate aims to provide consistent medication release over 24 hours, potentially eliminating this issue.
Data from a phase III clinical trial suggests that patients using the patch experienced symptom control for an average of 14 hours per day (compared to 8-10 hours with traditional oral medications). This extended coverage could particularly benefit adults in demanding work environments or students navigating long school days.
Management of Comorbid Conditions
ADHD often coexists with other mental health conditions. A study found that adult ADHD was highly comorbid with many other DSM-IV disorders and was associated with substantial role impairment. New combination therapies under investigation may offer more comprehensive treatment options.
The trial combining a stimulant with an alpha-2 agonist shows promise in managing both core ADHD symptoms and associated anxiety. Early results indicate a 30% reduction in anxiety symptoms compared to stimulant treatment alone. This approach could significantly improve outcomes for adults with ADHD who also experience anxiety disorders.
Personalized Treatment Approaches
The development of new ADHD medications opens up possibilities for more personalized treatment approaches. With a wider range of options available, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs, considering factors such as specific symptom profiles, comorbid conditions, and lifestyle requirements.
This personalized approach aligns with the growing trend towards precision medicine in mental health care. It allows for a more nuanced and effective management of ADHD, potentially leading to better overall outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Improved Medication Adherence
New formulations and delivery methods may also contribute to improved medication adherence. The convenience of once-daily dosing or patch application can simplify treatment regimens, making it easier for patients to consistently take their medication as prescribed.
Additionally, medications with fewer side effects are likely to be better tolerated, reducing the likelihood that patients will discontinue treatment due to adverse effects. This improved adherence can lead to more consistent symptom management and better long-term outcomes for individuals with ADHD.
Final Thoughts
The landscape of ADHD treatment will transform significantly by 2025. New ADHD medications in 2025 will offer more effective symptom management with fewer side effects. These advancements include innovative non-stimulant approaches, novel delivery methods, and promising combination therapies that will revolutionize patient care.

Healthcare providers will have greater flexibility to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs as more options become available. This personalized approach, combined with improved medication adherence, has the potential to enhance outcomes for individuals with ADHD. Patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals must stay informed about these emerging treatment options to make informed decisions about ADHD management.
Spark Mental Health provides personalized, evidence-based care for individuals with ADHD and other mental health conditions. Our telepsychiatry services offer convenient access to treatment, including medication management and cognitive-behavioral therapy. We will continue to stay at the forefront of treatment options (including new ADHD medications) to ensure our patients have access to the most effective and innovative care possible.






