Trauma can profoundly impact a person’s life, affecting their mental health, relationships, and overall well-being. At Spark Mental Health, we understand the importance of effective trauma therapy methods in helping survivors heal and reclaim their lives.
In this post, we’ll explore evidence-based trauma therapy methods and complementary approaches that have shown promising results. By understanding these techniques, you’ll be better equipped to seek the right help and support on your journey to recovery.
What Is Trauma and How Does It Affect Us?
Defining Trauma
Trauma extends beyond a mere bad experience. It encompasses events that overwhelm our coping abilities, leaving lasting impacts on mental and physical health. Trauma manifests in various forms, affecting individuals differently.
Types of Trauma
Trauma presents itself in multiple ways:
- Single-event trauma: Life-threatening incidents like car accidents or natural disasters.
- Complex trauma: Ongoing abuse or neglect.
- Military trauma: Experiences faced by combat veterans.
- Vicarious trauma: Repeated exposure to others’ traumatic experiences (often affecting first responders).
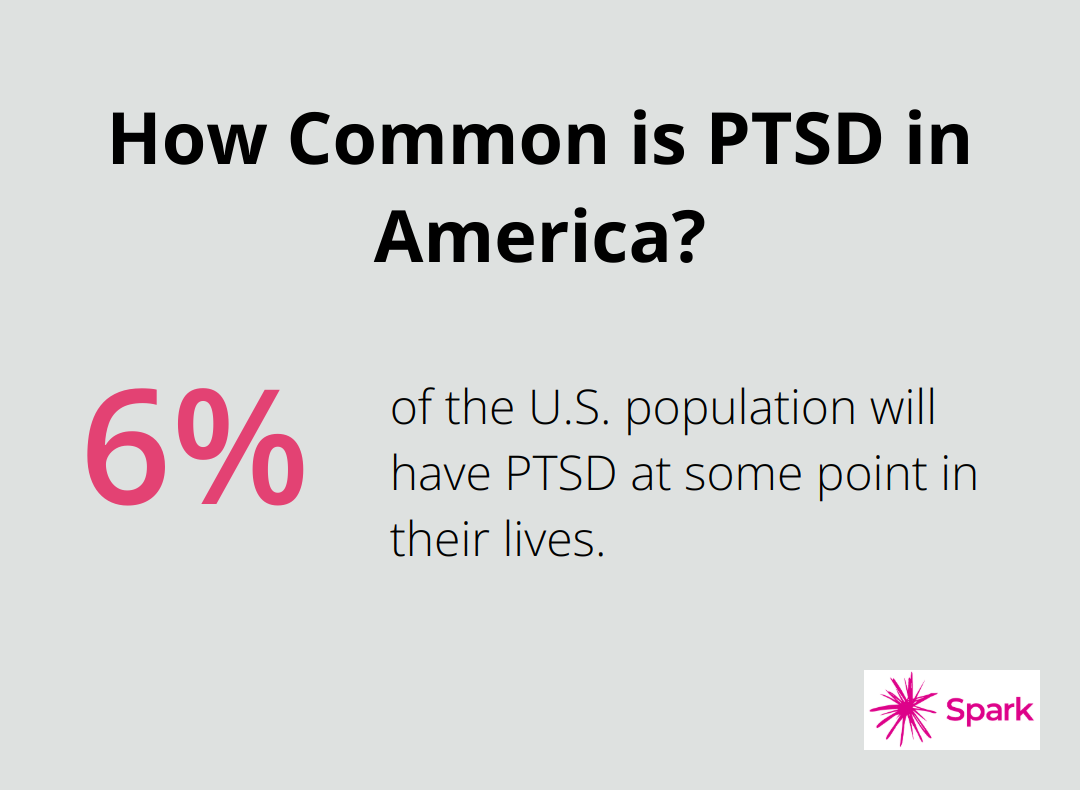
The National Center for PTSD reports that about 6 out of every 100 people (or 6% of the U.S. population) will have PTSD at some point in their lives, highlighting the prevalence of trauma-related disorders.
The Brain’s Response to Trauma
Trauma significantly impacts brain function:
- The amygdala (the brain’s alarm system) becomes hyperactive, leading to constant hypervigilance.
- The hippocampus (responsible for memory processing) can malfunction, resulting in fragmented or intrusive traumatic memories.
Research indicates that traumatic stress has a broad range of effects on brain function and structure, as well as on neuropsychological components of memory, explaining why survivors often struggle with emotional regulation and decision-making long after the traumatic event.
Physical and Emotional Symptoms
Trauma affects both mind and body:
Physical symptoms:
- Chronic pain
- Digestive issues
- Sleep disturbances
Emotional symptoms:
- Intense anxiety
- Depression
- Mood swings
One of trauma’s most challenging aspects is its ability to disrupt relationships. Many survivors face trust issues or repeat unhealthy patterns in their interactions.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Trauma
Untreated trauma can lead to various long-term effects:
- Substance abuse as a coping mechanism
- Difficulties maintaining employment
- Increased risk of developing other mental health conditions
It’s important to note that these symptoms don’t reflect character flaws or weaknesses. They represent normal responses to abnormal situations. With appropriate support and treatment, healing from trauma and reclaiming one’s life becomes possible.
As we explore effective trauma therapy methods in the next section, we’ll discover how evidence-based approaches can address these complex symptoms and promote healing.
Proven Trauma Therapy Techniques
Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT)
CPT stands as a powerful tool in trauma recovery. This method helps patients identify and challenge unhelpful thoughts related to their traumatic experiences. A typical CPT course involves 12 sessions, each lasting about an hour.
During CPT, patients learn to recognize how trauma affects their thinking patterns. They then work on developing more balanced and realistic perspectives. For example, a survivor might learn to challenge the belief that they’re to blame for their trauma.
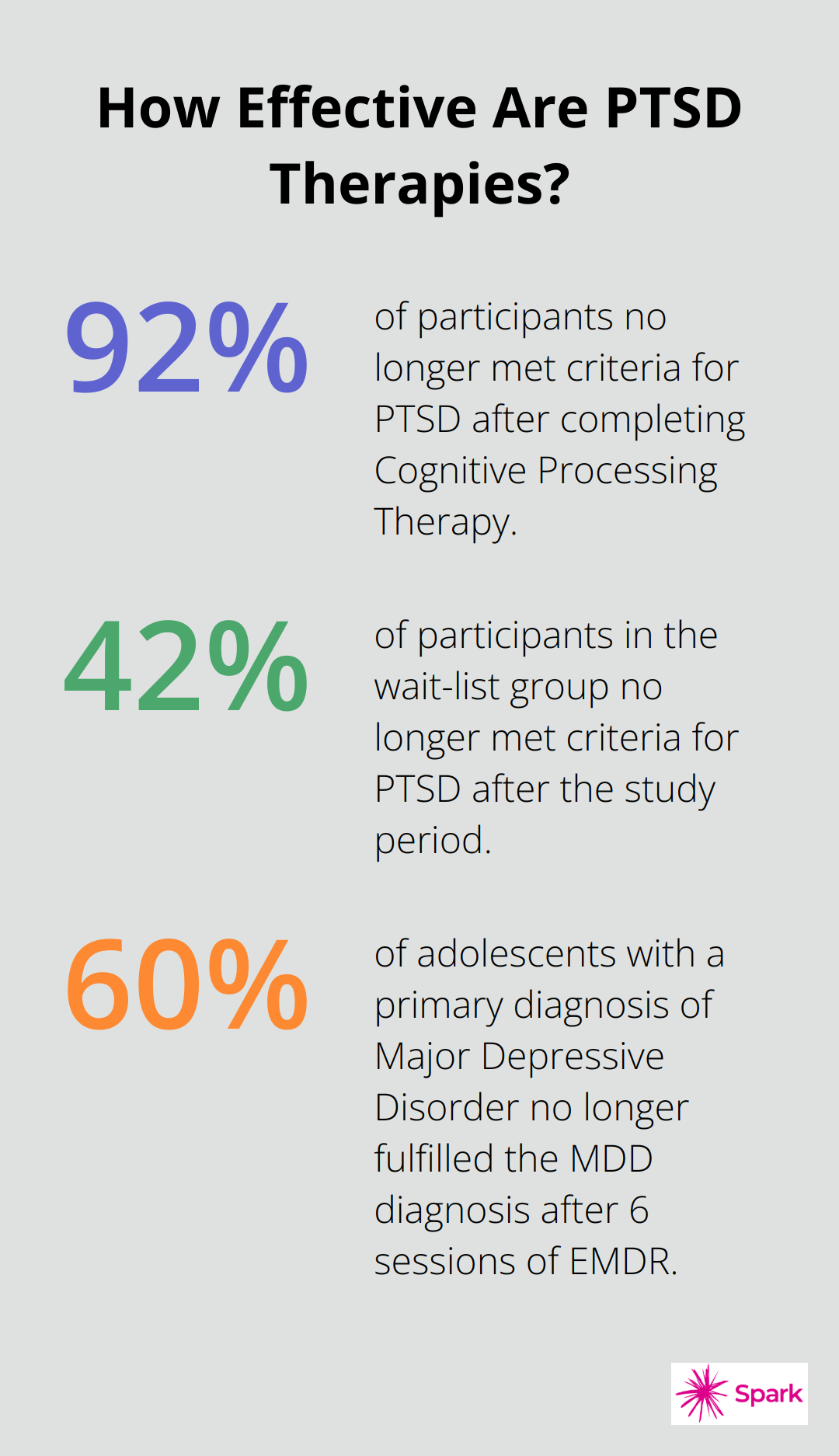
Research supports CPT’s effectiveness. A study found that 92% of participants no longer met criteria for PTSD after completing CPT, compared to 42% in the wait-list group. These gains were maintained at six-month follow-up.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR offers an innovative approach that doesn’t require extensive talking about the traumatic event. Instead, it uses bilateral stimulation (typically eye movements) while the patient briefly focuses on the trauma memory.
This method operates on the idea that traumatic memories are stored differently in the brain. EMDR aims to reprocess these memories, reducing their emotional impact. A standard EMDR treatment usually consists of 8-12 sessions.
The World Health Organization recognizes EMDR as an effective treatment for PTSD. A study found that 60% of adolescents with a primary diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) no longer fulfilled the MDD diagnosis after 6 sessions of EMDR.
Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE)
PE builds on the principle that avoiding trauma reminders perpetuates PTSD symptoms. This therapy gradually exposes patients to trauma-related memories, situations, or activities they’ve been avoiding.
A typical PE course lasts 8-15 sessions. Patients learn breathing techniques for anxiety management and then progressively confront their fears in a safe, controlled environment. This exposure helps reduce the power of trauma-related triggers over time.
PE’s effectiveness is well-documented.
Narrative Exposure Therapy (NET)
NET proves particularly effective for individuals who’ve experienced multiple or complex traumas. This method involves creating a chronological narrative of the patient’s life, focusing on both traumatic and positive events.
During NET sessions, the therapist helps the patient construct a detailed, written account of their experiences. This process aids in contextualizing traumatic memories within the broader life story, reducing their emotional intensity.
These evidence-based methods offer hope for trauma survivors. Each method addresses different aspects of trauma, allowing for a tailored approach to individual needs. As we explore complementary approaches to trauma healing in the next section, we’ll see how these methods can work alongside traditional therapies to provide comprehensive support for recovery.
Enhancing Trauma Recovery: Complementary Approaches
The Power of Mindfulness in Trauma Healing
Mindfulness techniques offer remarkable benefits for trauma survivors. Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) appears to have beneficial effects in treating PTSD in veterans, with greater improvement observed in self-reported PTSD symptoms. Mindfulness practice helps individuals stay grounded in the present moment, which reduces the impact of intrusive thoughts and flashbacks.

To incorporate mindfulness into your daily routine, try this simple exercise: Set aside 5 minutes each day to focus on your breath. When your mind wanders, gently redirect your attention back to your breathing. This practice can calm your nervous system and improve emotional regulation.
Body-Based Therapies for Trauma Recovery
Trauma often leaves an imprint on the body, making body-based therapies essential for comprehensive healing. Somatic experiencing, developed by Dr. Peter Levine, focuses on releasing traumatic shock, which is key to transforming patterns that get stuck and impact people’s daily life.
Yoga has also shown promising results in trauma recovery. A 2014 study in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that yoga significantly reduced PTSD symptoms in women with chronic, treatment-resistant PTSD. Try to incorporate a trauma-sensitive yoga practice into your routine, starting with just 10 minutes a day.
Art and Music Therapy: Expressing the Inexpressible
Art and music therapies provide unique avenues for processing traumatic experiences, especially when words feel inadequate. These creative approaches help externalize difficult emotions and memories, facilitating healing in a non-verbal way.
A study in the Journal of Trauma & Dissociation revealed that art therapy reduced PTSD symptoms and improved overall mental health in trauma survivors. You don’t need to be an artist to benefit from this approach. Start by dedicating 15 minutes a day to free-form drawing or coloring, allowing your emotions to guide your creative expression.
Group Therapy and Support Groups
Group therapy and support groups offer valuable opportunities for trauma survivors to connect with others who have similar experiences. These settings provide a safe space to share, learn coping strategies, and build a supportive community.
Research published in the Journal of Traumatic Stress found that group therapy can significantly reduce PTSD symptoms and improve overall functioning. Many survivors find comfort in knowing they’re not alone in their struggles (and triumphs).
Integrating Complementary Approaches with Professional Treatment
While these complementary approaches can be powerful tools in your recovery journey, they work best when combined with professional trauma therapy. A comprehensive treatment plan (tailored to your unique needs) often integrates evidence-based therapies with complementary approaches for optimal results.
Final Thoughts
Trauma therapy methods offer hope and healing for survivors. Evidence-based approaches like Cognitive Processing Therapy and EMDR, combined with complementary techniques such as mindfulness and art therapy, provide numerous paths to recovery. Professional help plays a vital role in the healing process, as trained therapists can create personalized treatment plans tailored to unique experiences and needs.

The journey to healing starts with a single step. You have the strength to overcome trauma’s impact and reclaim your life. The path may challenge you, but with the right support and resources, you can move towards a brighter future.
At Spark Mental Health, we offer personalized, evidence-based telepsychiatry services for conditions including PTSD. Our flexible online scheduling allows you to access treatment from home, using your smartphone or other devices. We provide individualized care plans, medication management, and cognitive-behavioral therapy to support your mental health journey.






